목적:
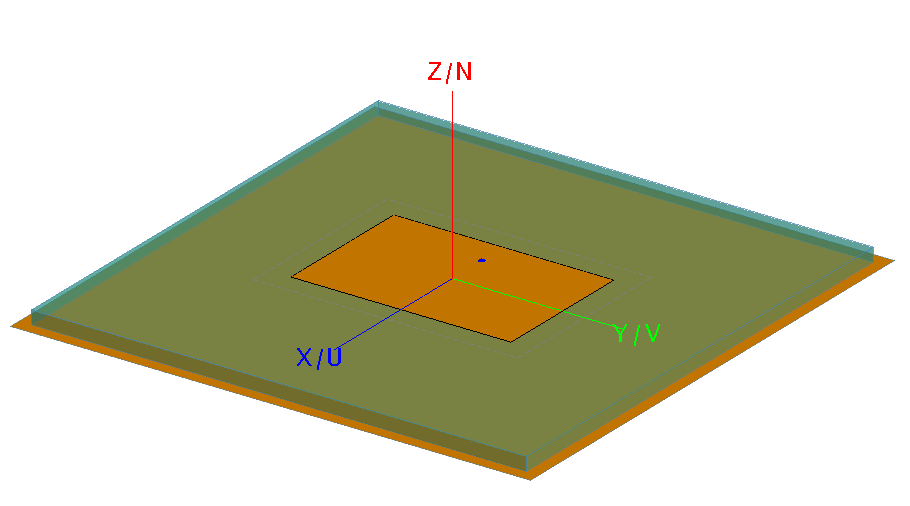
이번 예제는 pin feed 급전방식에 따른 패치안테나를 설계 및 해석할 것 입니다. 또한 Dielectric substrate은 Planar multilayer substrate(무한평면)을 사용하여 finite ground(유한평면)모델과의 시간과 메모리 사용량을 비교 진행할 것 입니다. 아래의 그림1.과 같은 모델이며 주파수는 2.7 – 3.3GHz에서 작동되는 패치 안테나 입니다. (초록색: planar multilayer substrate – infinite ground, 주황색: patch)
그림1.
모델정보:
- 패치길이(X방향): 31.1807
- 패치길이(Y방향): 46.7480
- 패치물성: PEC
- Substrate: 2.2 (relative permittivity)
- 단위: mm (millimeter)
입력변수:
- epsr = 2.2 (The relative permittivity of the substrate)
- freq = 3e9 (Operating frequency)
- lambda = c0/freq*1e3 (Free space wavelength)
- lengthX = 31.1807 (The length of the patch in the X direction)
- lengthY = 46.7480 (The length of the patch in the Y direction)
- offsetX = 8.9 (The location of the feed)
- substrateHeight = 2.87 (The height of the substrate)
- fmin = 2.7e9 (The minimum frequency in the simulation range)
- fmax = 3.3e9 (The maximum frequency in the simulation range)
- feedlineWidth = 4.5 (The width of the feedline for the microstrip model feed)
- substrateLengthX = 50 (The length of the substrate in the X direction)
- substrateLengthY = 80 (The length of the substrate in the Y direction)
- substrateHeight = 2.87 (The height of the substrate)
1. Pin-fed, Finite plane
첫 번째 예제는 feed pin 및 finite plane(유한평면)으로 모델링을 하여 진행합니다. 모델구성 및 절차는 아래의 과정을 참고하여 주시기 바랍니다.
모델구성(Finite plane):
- 모델단위 변경: m(meter) > mm(millimeter)
- 패치(patch)생성: rectangle, base centre, (0,0,0), width=lengthX, depth=lengthY, label=patch
- 급전선(feeding pin)생성: line, (-offsetX,0,0), (-offsetX,0,-substrateHeight), label=pin, 그림 참고
- 포트생성 위치: pin, Middle, label=Port1
- 전압인가: wire port1, 1[V], 50[Ohm]
- Union: patch, pin
- Dielectric 생성: relative permittivity=epsr, label=substrate
- Finite plane생성: Cuboid, Base corner, (-substrateLengthX/2, -substrateLengthY/2, -substrateHeight), (substrateLengthX, substrateLengthY, substrateHeight), label=substrate
- Union: pin, patch, substrate
- Dielectric 지정: substrate(region)=substrate, PEC=patch, substrate(ground face)
 그림2.
그림2.- 주파수 입력: Continuous frequency range=(fmin, fmax)
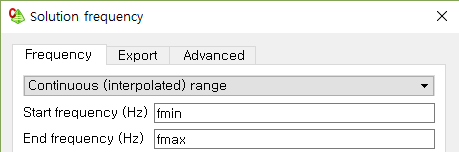 그림3.
그림3.- 대칭조건(Magnetic symmetry): Y=0 plane
- 결과추출조건(far field, E plane): -90, with , Increment 2
- 결과추출조건(far field, H plane): -90, with , Increment 2
- Mesh 생성: standard, segment radius=0.25
2. Pin-fed, Planar multilayer substrate
두 번째 예제는 feed pin 및 Planar multilayer substrate(무한평면)으로 모델링을 하여 진행합니다. 모델구성 및 절차는 아래의 과정을 참고하여 주시기 바랍니다.
모델구성(Infinite Plane):
- Finite plane 삭제
- planar multilayer substrate(무한평면): 그림참고
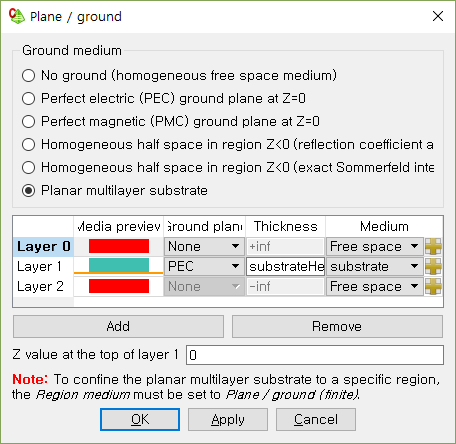 그림4.
그림4.- Dielectric 지정: PEC=(patch, ground), substrate=layer1
- 이후의 과정은 Finite plane 설정과 동일
해석결과:
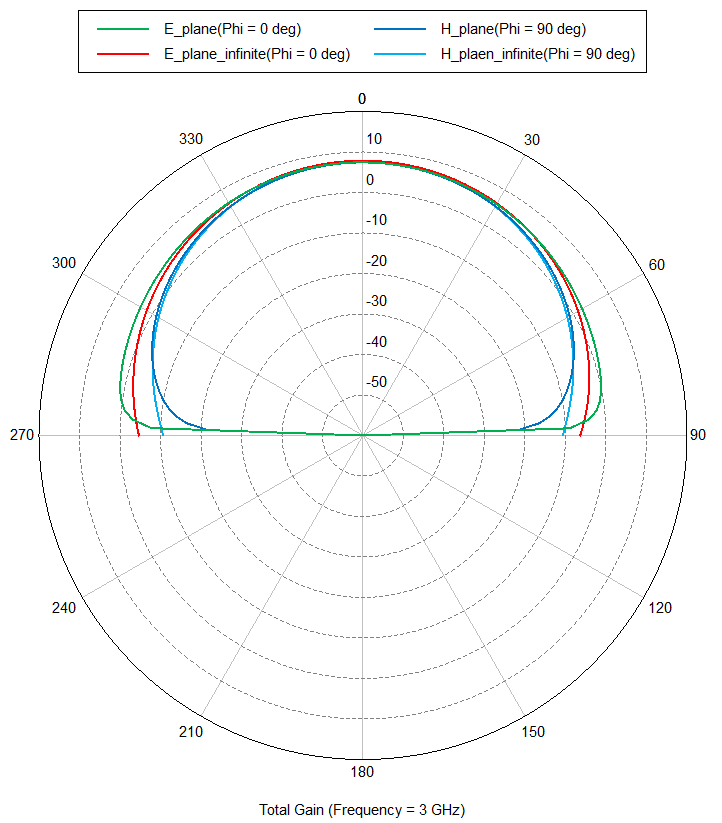
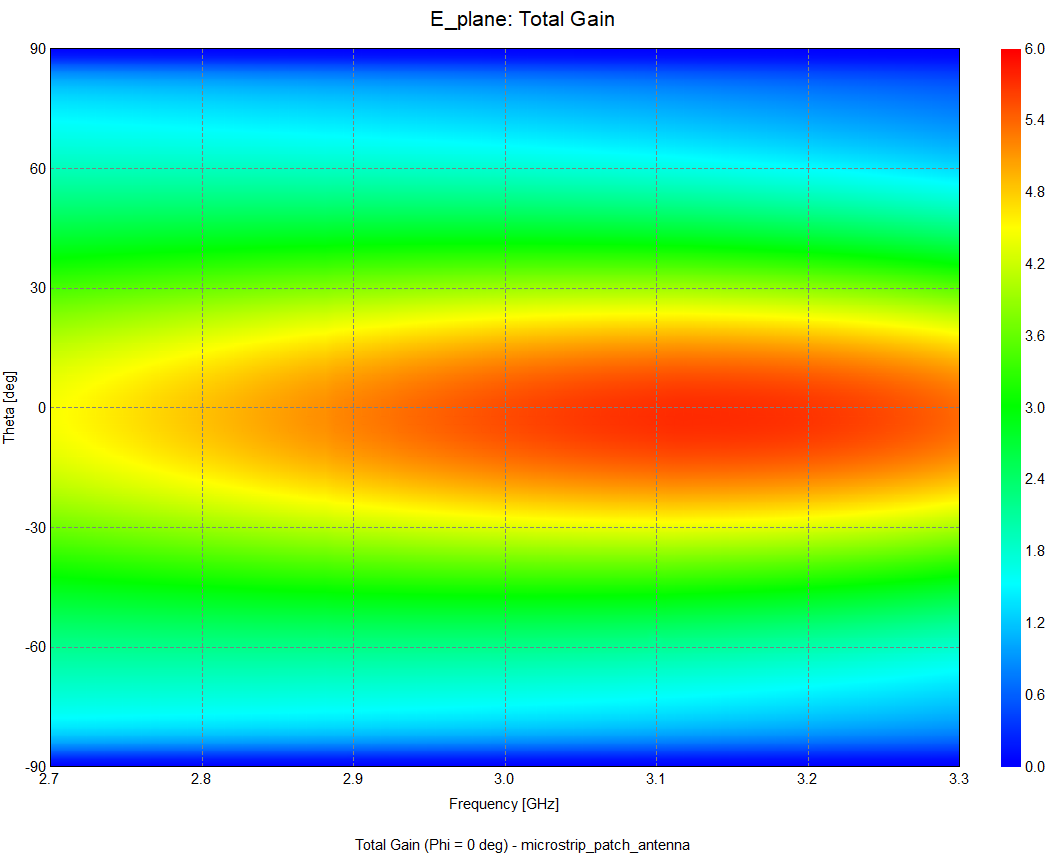
- 3GHz에서 Polar plot을 통해 E와 H 평면에 대한 gain[dB]을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 결론적으로 Infinite plan과 finite plane의 결과가 거의 같음을 확인할 수 있습니다. 따라서 finite plane 보다는 infinite plane을 이용하여 효율적인 해석을 할 수 있습니다.
- 해석시간의 경우 .out 파일을 통하여 finite/infinite plane을 비교할 수 있습니다.
finite plane
infinite plane
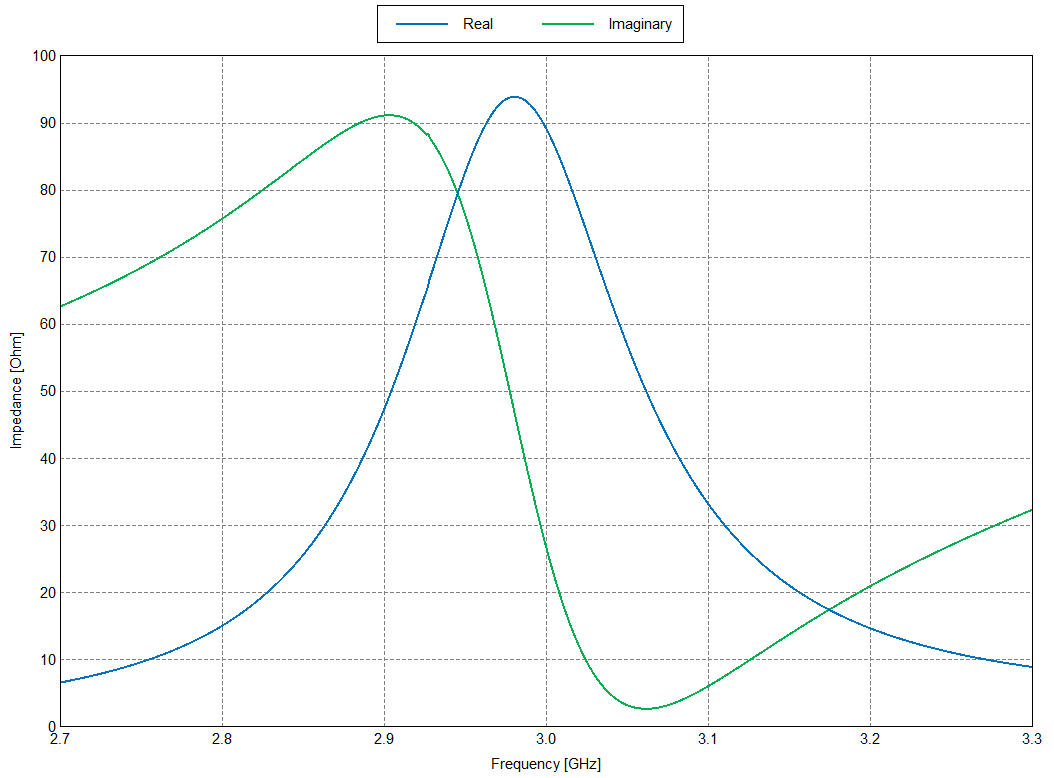
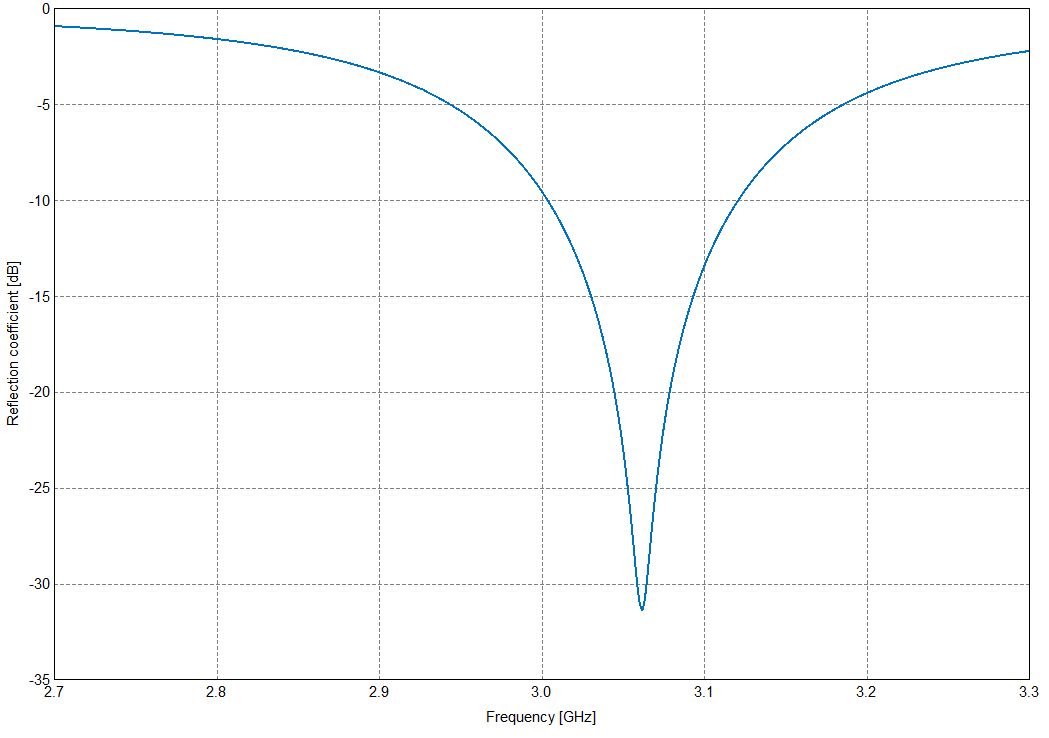
- Cartesian graph를 통해 Impedance[Ohm]와 Reflection coefficient[dB]를 확인하실 수 있습니다.
- 추가적으로 주파수 대역에 대한 Gain의 세기를 contour를 통하여 확인하실 수도 있습니다.
- 위의 내용은 FEKO Student Edition 버전을 통해서도 직접 실행하여 보실 수 있습니다.